The Chemistry of Lust: The Power of Dopamine and Testosterone 💥
Lust is the rawest form of desire, rooted in primal instincts and governed by the brain’s reward system. When you see someone you find sexually attractive, your brain releases a surge of dopamine 🎉, the neurotransmitter responsible for pleasure and motivation. This chemical flood is what makes flirting, seduction and sex feel exhilarating and addictive.
Additionally, testosterone the hormone associated with libido plays a key role in sexual attraction. While both men and women produce testosterone, higher levels are linked to an increased sex drive, greater risk-taking and a stronger pursuit of pleasure. The spike in testosterone and dopamine creates the craving for physical intimacy, igniting the fire of lust 🔥🔥
The Spark of Attraction: The Role of Adrenaline, Serotonin and PEA ⚡💖
Attraction goes beyond physical desire it’s the moment when your heart races, palms sweat and you can’t stop thinking about that one special person. This stage is fueled by adrenaline (also known as epinephrine) ⚡, which triggers the classic symptoms of excitement and nervousness when you’re around someone you’re infatuated with.
At the same time, phenylethylamine (PEA) a natural amphetamine-like chemical heightens the euphoria and obsession we feel in the early stages of attraction. PEA increases energy, sharpens focus and creates an almost addictive high when you’re falling for someone 💓
However, the paradox of attraction is that serotonin levels actually drop during this phase. Serotonin is the neurotransmitter that stabilizes mood and lower levels explain why people in the throes of new love often display obsessive thinking, idealizing their partner and even losing sleep over them 😍💭
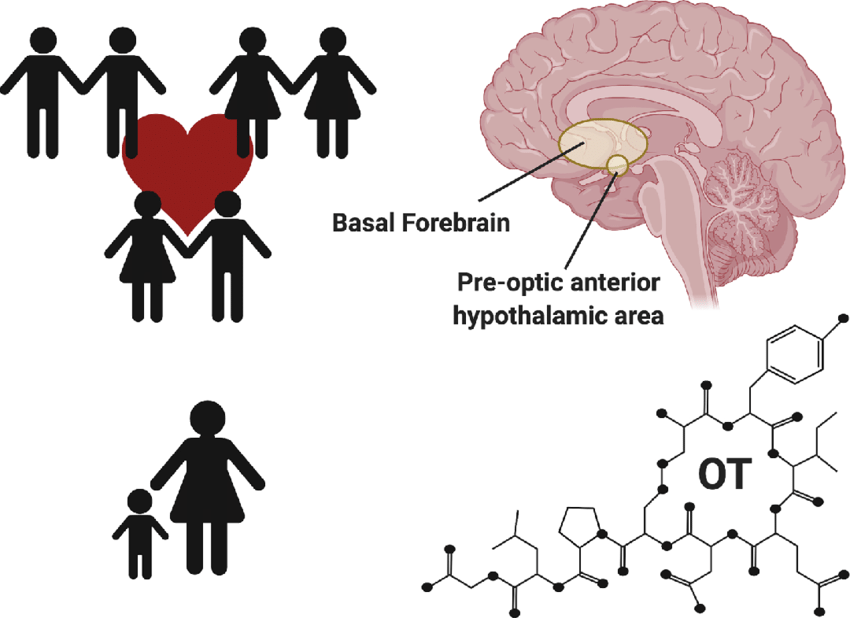
The Deep Bond of Love: The Power of Oxytocin and Vasopressin 🤗❤️
While lust and attraction are fleeting, long-term love is built on a foundation of deep emotional connection and trust. This stage is driven by oxytocin, often called the “love hormone” or “cuddle chemical.” Released during physical touch, sex and orgasm, oxytocin fosters emotional bonding, reducing stress and increasing feelings of intimacy and security 🤗
Similarly, vasopressin plays a crucial role in long-term attachment. Studies have shown that vasopressin influences monogamy and commitment, particularly in men. Higher levels of vasopressin have been linked to stronger relationship bonds, emotional fidelity and a sense of responsibility toward a partner 🔗💏
Why We Desire: Evolutionary Psychology and the Purpose of Passion 🧬
Desire isn’t just about pleasure it’s deeply rooted in our evolutionary survival. The biological goal of lust is reproduction, ensuring the continuation of the species. Attraction serves the purpose of selecting the best mate based on genetic compatibility, health and social status. Love, in turn, fosters pair bonding, increasing the chances of raising offspring in a stable environment 👶💕
Interestingly, the qualities we find desirable are often subconscious indicators of reproductive fitness. For example, symmetrical facial features, a certain waist-to-hip ratio, or a deep voice in men can signal genetic strength and fertility. This explains why physical attraction can sometimes feel instant and involuntary ✨
Can We Hack Desire? The Psychology of Attraction and Connection 🕵️♀️💑
While chemistry and biology play a significant role in desire, there are ways to consciously enhance attraction and deepen emotional connection:
- Eye Contact 👀: Prolonged eye contact increases feelings of attraction and intimacy by stimulating oxytocin release.
- Mirroring 🪞: Subtly mimicking your partner’s body language builds subconscious trust and connection.
- Surprise and Novelty 🎭: Engaging in new experiences together keeps dopamine levels high, rekindling passion over time.
- Physical Touch 🤲: Regular affectionate touch, even small gestures like holding hands, reinforces the bond between partners.